
cardioversion – where the heart is given a controlled electric shock to restore normal rhythm.medicines to control the heart rate or rhythm.medicines to prevent a stroke (people with atrial fibrillation are more at risk of having a stroke).Treating atrial fibrillationĪtrial fibrillation is not usually life threatening, but it can be uncomfortable and often requires treatment. Our guide to care and support explains your options and where you can get support. care for someone regularly because they're ill, elderly or disabled (including family members).need help with day-to-day living because of illness or disability.
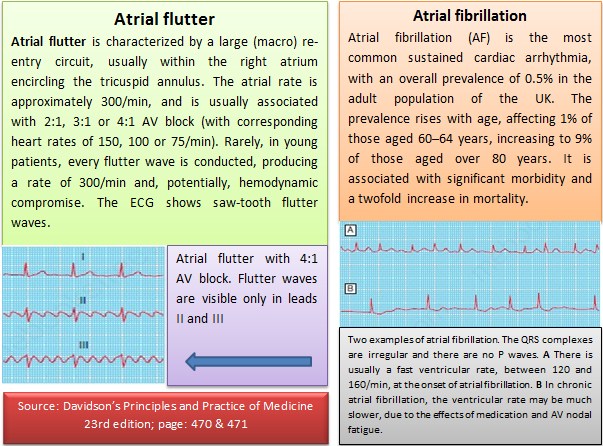
Information: Social care and support guide More men than women have atrial fibrillation.Ītrial fibrillation is more likely to occur in people with other conditions, such as high blood pressure (hypertension), atherosclerosis or a heart valve problem. It can affect adults of any age, but it's more common in older people. long-standing atrial fibrillation – where you've had atrial fibrillation usually for over a yearĪtrial fibrillation is the most common heart rhythm disturbance, affecting around 1.4 million people in the UK.permanent atrial fibrillation – when it's present all the time.persistent atrial fibrillation – each episode lasts for longer than 7 days (or less when it's treated).paroxysmal atrial fibrillation – episodes come and go, and usually stop within 48 hours without any treatment.It may be triggered by certain situations, such as drinking too much alcohol or smoking.Ītrial fibrillation can be defined in various ways, depending on the degree to which it affects you. The cause is not fully understood, but it tends to affect certain groups of people, such as older people and people living with long-term (chronic) conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure or obesity. These impulses override the heart's natural pacemaker, which can no longer control the rhythm of the heart. This causes you to have a highly irregular pulse rate. In atrial fibrillation, the heart's upper chambers (atria) contract randomly and sometimes so fast that the heart muscle cannot relax properly between contractions. This reduces the heart's efficiency and performance.Ītrial fibrillation happens when abnormal electrical impulses suddenly start firing in the atria.

This process is repeated every time the heart beats. They then relax so the heart can fill with blood again. When the heart beats normally, its muscular walls tighten and squeeze (contract) to force blood out and around the body. Call 999 immediately as you need immediate treatment in hospital. also started with shortness of breath, sweating and feeling or being sick.spreads to your arms, back, neck or jaw.

It's important to get medical advice to make sure it's nothing serious.
You can measure your heart rate by checking your pulse in your wrist or neck. Atrial fibrillation is a heart condition that causes an irregular and often abnormally fast heart rate.Ī normal heart rate should be regular and between 60 and 100 beats a minute when you're resting.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
